Brute force
Take max of all possible subarrays.
Products of all possible subarrays starting at a particular index can be computed in time. Since there are
possible starting indices, total time:
, space:
.
class Solution:
def maxProduct(self, nums):
n = len(nums)
largest_product = float('-inf')
for start in range(n):
current_product = 1
for end in range(start, n):
current_product *= nums[end]
largest_product = max(
largest_product,
current_product
)
return largest_product
Dynamic programming
Subproblem
Without negative numbers
Let be the largest product in
nums[0:i+1] for a subarray that includes nums[i]. Then, either nums[i] belongs to the subarray of or
nums[i]is the first element of a subarray.
Our solution is then . Because, say subarray
nums[i:j+1] has the largest product. When we computed ,
nums[i] must have started a new subarray. And all have been able to extend that subarray. So,
must have the product of
nums[i:j+1].
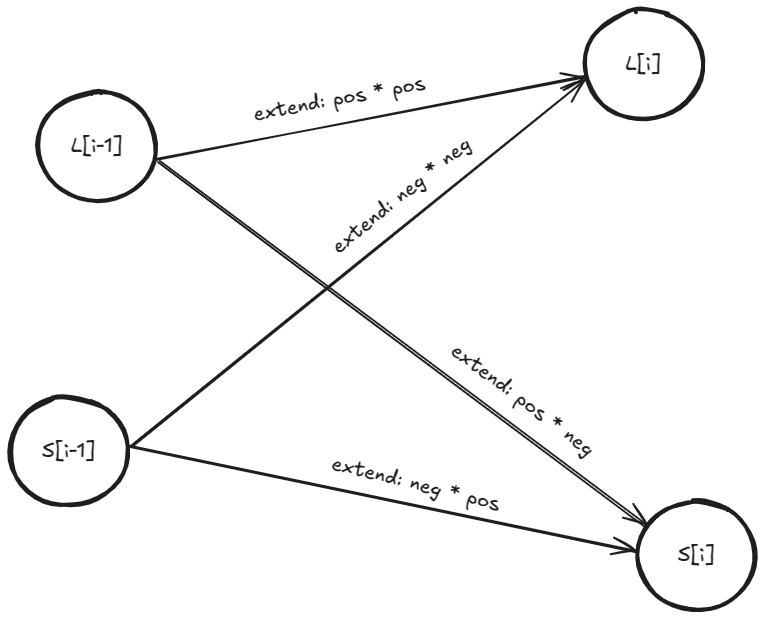
With negative numbers
Product of two negative numbers is positive. That adds another way for nums[i] to be a part of an earlier subarray. Let be the smallest product in
nums[0:i+1] for a subarray that includes nums[i]. Now, we can update to include negative-negative-gives-positive path:
Symmetrically, for , we include two extension paths: negative-times-positive and positive-times-negative:
Again, we find the solution as .
Order
Since edges always go from smaller indices to larger indices, we can process the numbers from left-to-right and have a topological ordering.
Time: , space:
.
class Solution:
def maxProduct(self, nums):
n = len(nums)
L, S = [0] * n, [0] * n
L[0], S[0] = nums[0], nums[0]
for i in range(1, n):
L[i] = max(
L[i-1] * nums[i],
S[i-1] * nums[i],
nums[i]
)
S[i] = min(
L[i-1] * nums[i],
S[i-1] * nums[i],
nums[i]
)
return max(L)
Since edges always go from index i+1 to index i, we can use a single variable instead of n-sized list.
Time: , space:
.
class Solution:
def maxProduct(self, nums):
n = len(nums)
L, S, global_L = nums[0], nums[0], nums[0]
for i in range(1, n):
L, S = max(L * nums[i], S * nums[i], nums[i]), min(
L * nums[i], S * nums[i], nums[i]
)
global_L = max(global_L, L)
return global_L
Leave a comment