Brute Force
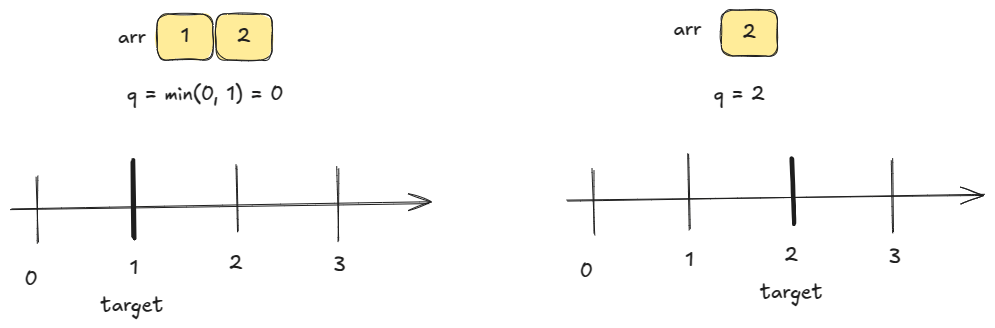
We need to find the best defined as:
. We break a tie in favor of smaller
.
Since all numbers in arr are positive integers, the domain of is
.
Time: , space:
.
class Solution:
def findBestValue(self, arr: List[int], target: int) -> int:
min_diff, best_q = float('inf'), float('inf')
for q in range(target+1):
capped_sum = sum( min(q, x) for x in arr )
diff = abs( target - capped_sum )
if diff > min_diff:
continue
best_q = min(best_q, q) if diff == min_diff else q
min_diff = diff
return best_q
Sort and search
We can break the inner sum to get rid of like:
. In the input
arr, these two cases are mixed. We can sort arr to separate them out. Then with binary-search, we can find these two regions and with a pre-computed cumsum, the inner loop takes .
Time: , space:
.
class Solution:
def find_insert_index(self, x, nums) -> int:
lo, hi = 0, len(nums)-1
while lo <= hi:
mid = (lo + hi) // 2
if nums[mid] < x:
lo = mid+1
else:
hi = mid-1
return lo
def find_capped_sum(self, q, arr, cumsum) -> int:
n = len(arr)
q_pos = self.find_insert_index(q, arr)
left_sum = cumsum[q_pos-1] if q_pos > 0 else 0
right_sum = (n - q_pos)*q
return left_sum + right_sum
def find_cumsum(self, nums) -> List[int]:
cumsum = [nums[0]] + [0] * (len(nums)-1)
for i, x in enumerate(nums[1:], start=1):
cumsum[i] = cumsum[i-1] + x
return cumsum
def findBestValue(self, arr: List[int], target: int) -> int:
arr.sort()
cumsum = self.find_cumsum(arr)
min_diff, best_q = float('inf'), float('inf')
for q in range(target+1):
capped_sum = self.find_capped_sum(q, arr, cumsum)
diff = abs( target - capped_sum )
if diff > min_diff:
continue
best_q = min(best_q, q) if diff == min_diff else q
min_diff = diff
return best_q
Given a target and arr of length , we have perfect size
— if we take
copies of this size we meet target perfectly. Since we are allowed to cap, as long as
arr has all numbers at least as big as , we are allowed to use
as our answer.
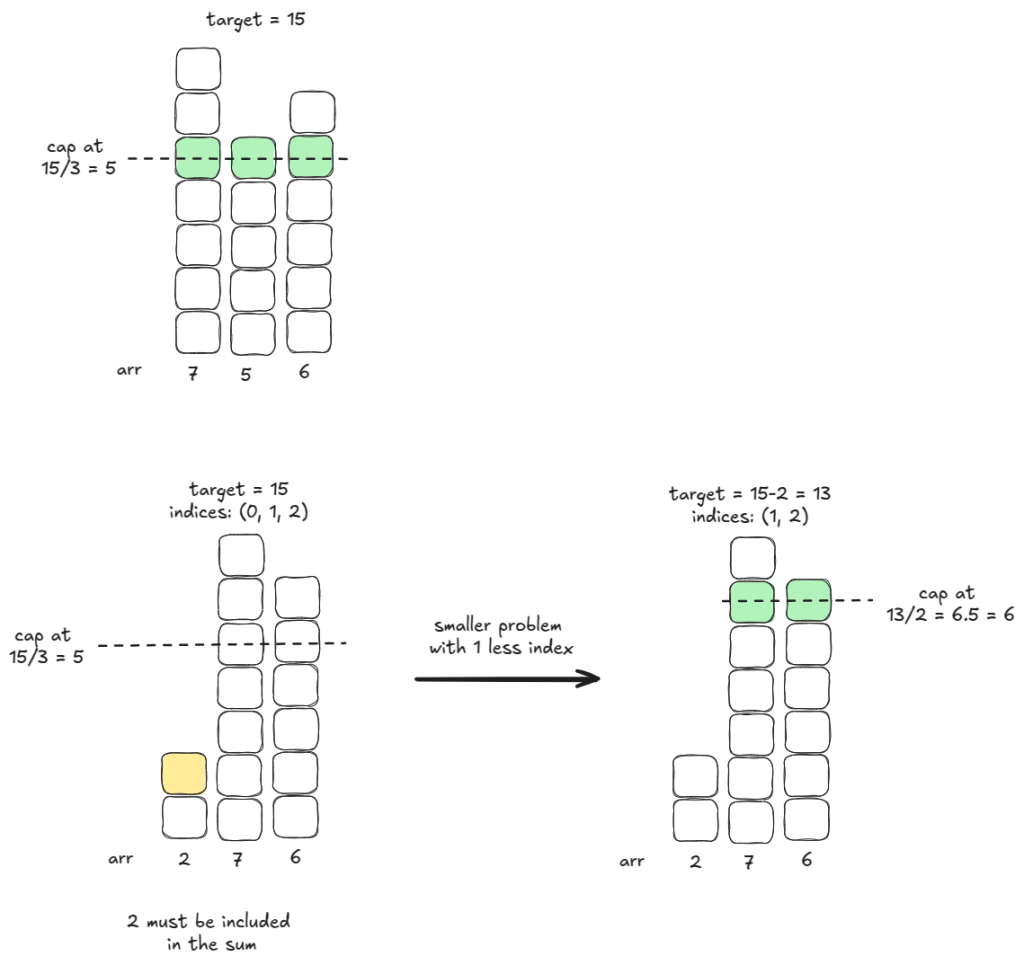
If a number in arr is smaller than , we have to include that number and find a perfect size for the remainder of the
arr. If arr was sorted, as soon as we find an allowed perfect size for the suffix arr[j:n+1], we can return the closest number to the perfect size as the answer.
Time: . Space:
.
class Solution:
def find_best(self, begin, arr, target) -> int:
if begin == len(arr):
return arr[-1]
x = arr[begin]
n = len(arr) - begin
if n*x < target:
return self.find_best(begin+1, arr, target-x)
x_fit = ceil( target/n - 0.5 )
return x_fit
def findBestValue(self, arr: List[int], target: int) -> int:
arr.sort()
return self.find_best(0, arr, target)
We can do it iteratively to save space.
Time: . Space: that of sorting.
class Solution:
def findBestValue(self, arr: List[int], target: int) -> int:
arr.sort()
n = len(arr)
for i, x in enumerate(arr):
ncopies = n-i
if ncopies * x < target:
# If x is too small, must include
target -= x
continue
return ceil(target/ncopies - 0.5)
return arr[-1]
Leave a comment