The complexity comes from flood cells, which grow over time. Since Manhattan distance from a flood cell is the minimum time it would take for a cell to get flooded, it is not difficult to find out which of my four neighboring cells will get flooded next. However, presence of stones, source, and destination blocks flooding — Manhattan distance is not sufficient.
Instead, if we look at the simulation, we see wavefronts growing radially outwards both from the flood cells and from source.
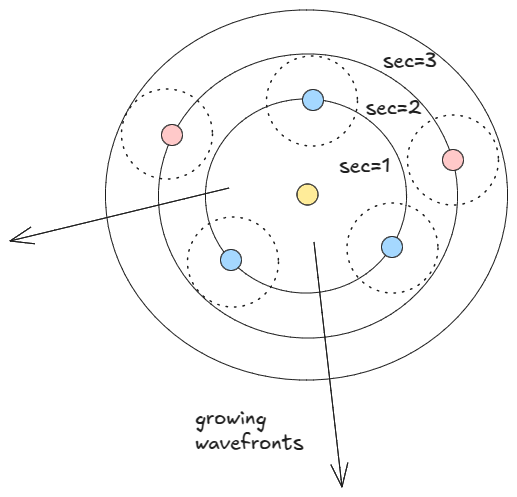
So, we do a single BFS with two queues containing the flooded cells and the source. One second passes in each iteration. Since a cell is forbidden if, it gets flooded at the same time as we land, in each iteration, we process the wavefront of the flood first. Then, in that iteration we process the wavefront originating from source. This way the source-wavefront sees the latest state of land while finding next move. As soon as the source wavefront finds the destination, we have got the minimum time.
Time is linear in the size of the graph: .
The set visited can be as large as the grid, so extra space is . We could assign say “V” to mark visited (taking care not to overwrite “D”) and then the extra space would be the size of the widest wavefront or
.
from itertools import product as cartesian
class Solution:
def neibors(self, u, m, n) -> List[Tuple[int]]:
r, c = u
deltas = [(0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -1), (-1, 0)]
edges = []
for dr, dc in deltas:
r2, c2 = r + dr, c + dc
if 0 <= r2 < m and 0 <= c2 < n:
edges.append((r2, c2))
return edges
def minimumSeconds(self, land: List[List[str]]) -> int:
m, n = len(land), len(land[0])
dst = None
q, flood_q = deque(), deque()
for r, c in cartesian(range(m), range(n)):
if land[r][c] == "D":
dst = (r, c)
elif land[r][c] == "S":
q.append((r, c))
elif land[r][c] == "*":
flood_q.append((r, c))
visited = {q[0]}
min_time_sec = 0
while q:
# process flood_q first to get latest view
# while finding next move
k = len(flood_q)
for _ in range(k):
u = flood_q.popleft()
for v in self.neibors(u, m, n):
r, c = v
if (
land[r][c] == "S"
or land[r][c] == "D"
or land[r][c] == "X"
or land[r][c] == "*"
):
continue
# flood the cell
land[r][c] = "*"
flood_q.append(v)
l = len(q)
for _ in range(l):
u = q.popleft()
# Only way to find a solution
if land[u[0]][u[1]] == "D":
return min_time_sec
for v in self.neibors(u, m, n):
if v in visited:
continue
r, c = v
if land[r][c] == "X" or land[r][c] == "*":
continue
visited.add(v)
q.append(v)
min_time_sec += 1
return -1
Leave a comment