Recursive
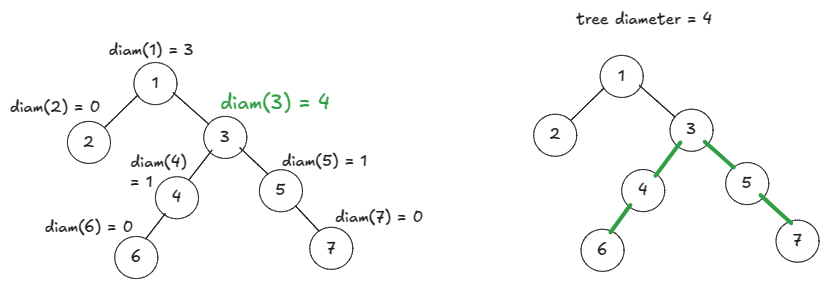
Diameter is the edge count along the longest path. The longest path going through a node can have parts from both left and right subtrees.
It is hard to define diameter going through a node in terms of diameter of its children. .
However, it is easy to define in terms of height of
‘s children.
. And, height of a node is easy to define recursively:
.
So, we recursively find height of a node and piggyback on that recursion to compute the length of the longest path that goes through the node. Diameter of the tree is then the max such length.

Time: , space:
.
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def diameterOfBinaryTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
max_diameter = float("-inf")
def height(u: TreeNode) -> int:
nonlocal max_diameter
if not u:
return 0
left_height = height(u.left)
right_height = height(u.right)
diameter = left_height + right_height
max_diameter = max(max_diameter, diameter)
return max(left_height, right_height) + 1
# Piggyback on height() recursion to compute diameter
_ = height(root)
return max_diameter
Iterative
The recursion unwinds first and does the computation on the return path, bottom-up. So, with an explicit stack and visited set, we do the unwinding and compute on the return path as well. For each node we keep its computed height in a dict. Second time we visit a node, it is in the return path, so by then height of its children have been computed and available in the dict.
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def diameterOfBinaryTree(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
max_diameter = 0
height = {}
visited = set()
stack = [root]
while stack:
top = stack.pop()
if top not in visited:
visited.add(top)
stack.extend(u for u in (top, top.right, top.left) if u)
continue
# Return path, by now height of top's children have been computed
left_height = height[top.left] if top.left else 0
right_height = height[top.right] if top.right else 0
height[top] = max( left_height, right_height ) + 1
diameter = left_height + right_height
max_diameter = max( max_diameter, diameter )
return max_diameter
Leave a comment