Recursive
In the binary tree, there are two types of path: (1) linear (2) curved. Sum on a linear path may contribute to parent’s sum. Sum on a curved path does not contribute to parent’s sum.
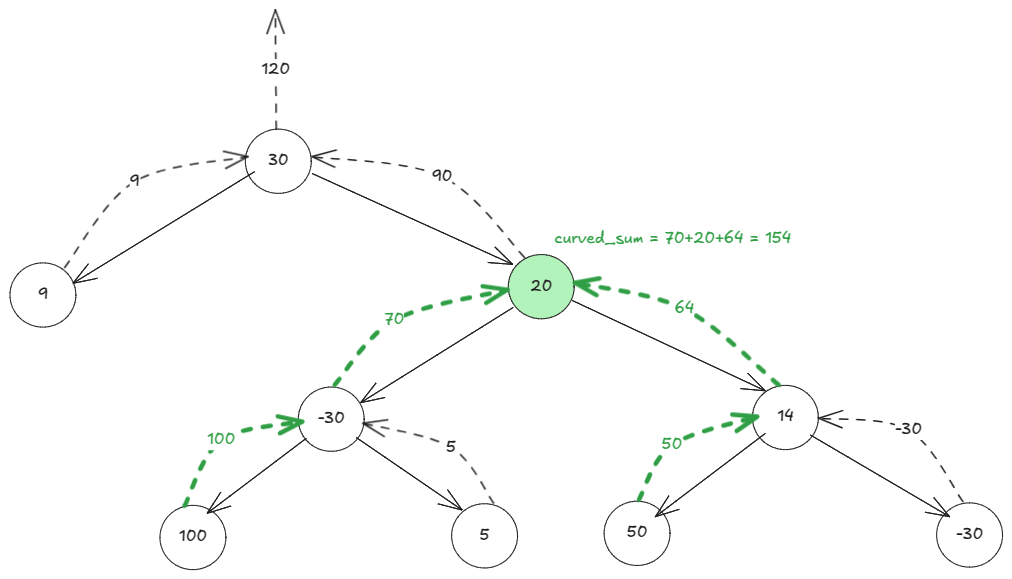
Say is the linear sum of the node
— sum on a linear path that ends at
. So,
must include
but including
or
is optional.
On the other hand, if is the curved sum:
Then the max path sum of the tree is .
We recursively compute keeping track of max
bottom-up. For
we piggyback on the same recursion.
Time: , space:
.
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def maxPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
max_curved_sum = float("-inf")
max_linear_sum = float("-inf")
def compute_linear_sum(u) -> int:
nonlocal max_curved_sum, max_linear_sum
if not u:
return 0
left_linear_sum = compute_linear_sum(u.left)
right_linear_sum = compute_linear_sum(u.right)
max_child_linear_sum = max( left_linear_sum, right_linear_sum )
linear_sum = max( max_child_linear_sum+u.val, u.val )
max_linear_sum = max( max_linear_sum, linear_sum )
curved_sum = left_linear_sum + u.val + right_linear_sum
max_curved_sum = max( max_curved_sum, curved_sum )
return linear_sum
_ = compute_linear_sum(root)
return max(max_curved_sum, max_linear_sum)
Iterative
With explicit stack we simulate the bottom-up recursion using visited set and linear_sums dict. Second time we visit a node, on the return path, the linear sums of its children have already been computed.
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def maxPathSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
max_curved_sum = float("-inf")
max_linear_sum = float("-inf")
visited = set()
linear_sums = {}
stack = [root]
while stack:
u = stack.pop()
if u not in visited:
visited.add(u)
stack.extend( v for v in (u, u.left, u.right) if v )
continue
# Return path: linear sums of u's children are available
left_linear_sum = linear_sums[u.left] if u.left else 0
right_linear_sum = linear_sums[u.right] if u.right else 0
max_child_linear_sum = max( left_linear_sum, right_linear_sum )
linear_sum = max( u.val, max_child_linear_sum + u.val )
linear_sums[u] = linear_sum
max_linear_sum = max( max_linear_sum, linear_sum )
curved_sum = left_linear_sum + u.val + right_linear_sum
max_curved_sum = max( max_curved_sum, curved_sum )
return max( max_curved_sum, max_linear_sum )
Leave a comment