Recursive
We do DFS preferring right. With root , the left subtree contributes to the right-side view only if, it is deeper than the right subtree. In that case, prefix of view is from right subtree and suffix of view is from left subtree. We pass around depth to decide if left subtree should contribute.
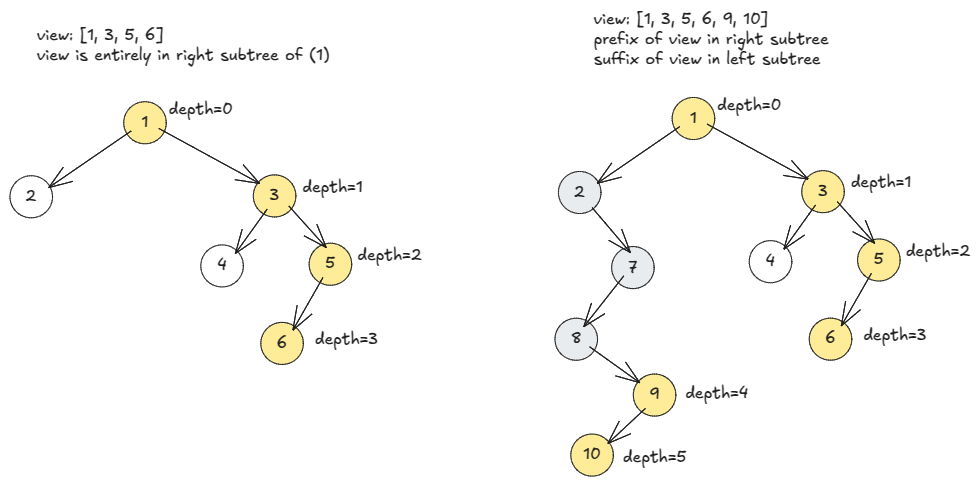
Time: , space:
.
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def dfs(self, root, view, depth) -> List[int]:
if not root:
return
if depth == len(view):
view.append(root.val)
self.dfs(root.right, view, depth+1)
self.dfs(root.left , view, depth+1)
def rightSideView(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:
view = []
self.dfs(root, view, 0)
return view
Iterative
Simulate top-down depth based recursion with an explicit stack.
Time: , space:
.
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def rightSideView(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:
if not root:
return []
view = []
stack = [(root, 0)]
while stack:
u, depth = stack.pop()
if depth == len(view):
view.append(u.val)
stack.extend( (c, depth+1) for c in (u.left, u.right) if c )
return view
Rightmost node on each level belongs to the right-side view.
Time: , space:
.
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def rightSideView(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[int]:
if not root:
return []
view = []
q = deque([root])
while q:
view.append(q[-1].val)
level_len = len(q)
for _ in range(level_len):
u = q.popleft()
q.extend(c for c in (u.left, u.right) if c)
return view
Leave a comment