Unidirectional BFS
The problem is to find the shortest path in an undirected word graph from beginWord to endWord. An edge means:
is a word in
wordList and Hamming distance between the words and
is 1.
We use BFS. Say and
are the vertex and edge sets of the word graph. Here,
. If word length is
, producing adjacency list of a vertex takes time
.
Time: , space:
.
class Solution:
def adj_list(self, u: str, word_set: Set[str]) -> Set[str]:
neibors = set()
for w in word_set:
hamming_dist = sum(1 if x != y else 0 for x, y in zip(u, w))
if hamming_dist != 1:
continue
neibors.add(w)
return neibors
def ladderLength(self, beginWord: str, endWord: str, wordList: List[str]) -> int:
word_set = set( wordList )
level = 0
visited = {beginWord}
q = deque([beginWord])
while q:
level_len = len(q)
for _ in range(level_len):
u = q.popleft()
if u == endWord:
return level+1
for v in self.adj_list(u, word_set):
if v in visited:
continue
visited.add(v)
q.append(v)
level += 1
return 0
Since alphabet size is 26, for a vertex we could produce all words with Hamming distance = 1 and check if it is in . The cost of producing adjacency list of a vertex is then
— including copy.
Time: , space:
.
class Solution:
def adj_list(self, u: str, word_set: Set[str]) -> Set[str]:
neibors = set()
u_copy = list(u)
for i, u_c in enumerate(u):
for c in ( chr( ord("a")+j ) for j in range(26) ):
if c == u_c:
continue
u_copy[i] = c
nei = "".join(u_copy)
if nei in word_set:
neibors.add(nei)
u_copy[i] = u_c
return neibors
def ladderLength(self, beginWord: str, endWord: str, wordList: List[str]) -> int:
word_set = set( wordList )
level = 0
visited = {beginWord}
q = deque([beginWord])
while q:
level_len = len(q)
for _ in range(level_len):
u = q.popleft()
if u == endWord:
return level+1
for v in self.adj_list(u, word_set):
if v in visited:
continue
visited.add(v)
q.append(v)
level += 1
return 0
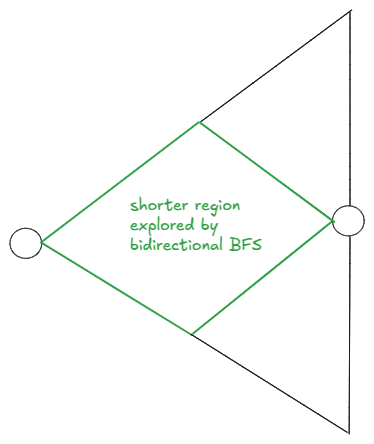
Bi-directional BFS
We can do two BFSes at the same time: (1) from beginWord (2) from endWord. At any iteration, if the wavefronts of the two BFSes have a common word say , we know the shortest path is:
. We end up exploring a shorter region.
from typing import List, Set
class Solution:
def adj_list(self, u: str, word_set: Set[str]) -> Set[str]:
neibors = set()
u_copy = list(u)
for i, u_c in enumerate(u):
for c in (chr(ord("a") + j) for j in range(26)):
if c == u_c:
continue
u_copy[i] = c
nei = "".join(u_copy)
if nei in word_set:
neibors.add(nei)
u_copy[i] = u_c
return neibors
def bfs(self, source, words) -> Set[str]:
# We remove a word after it has been visited.
# So, word_set implicitly tracks visited words.
word_set = set(words)
wavefront = {source}
word_set.discard(source)
while wavefront:
next_front = set()
for u in wavefront:
for v in self.adj_list(u, word_set):
next_front.add(v)
word_set.remove(v)
wavefront = next_front
yield wavefront
def ladderLength(self, beginWord: str, endWord: str, wordList: List[str]) -> int:
if endWord not in wordList:
# Even if endWord isn't in the wordList
# the back BFS will start with endWord
# and may falsely declare a path.
return 0
step = 1
front, back = {beginWord}, {endWord}
for new_front, new_back in zip( self.bfs(beginWord, wordList), self.bfs(endWord, wordList) ):
if new_front & back:
return step+1
if front & new_back:
return step+1
if new_front & new_back:
return step+2
front, back = new_front, new_back
step += 2
return 0
With zip(), we are producing two new wavefronts at each iteration. Along with the older back and front, we thus end up keeping four wavefronts per iteration. Instead, we can advance only the smaller of the two wavefronts at each iteration. That way:
- We shall keep only two wavefronts per iteration
- Growth of wavefront remains low.
from typing import List, Set
class Solution:
def adj_list(self, u: str, word_set: Set[str]) -> Set[str]:
neibors = set()
u_copy = list(u)
for i, u_c in enumerate(u):
for c in (chr(ord("a") + j) for j in range(26)):
if c == u_c:
continue
u_copy[i] = c
nei = "".join(u_copy)
if nei in word_set:
neibors.add(nei)
u_copy[i] = u_c
return neibors
def bfs(self, source, words) -> Set[str]:
# We remove a word after it has been visited.
# So, word_set implicitly tracks visited words.
word_set = set(words)
wavefront = {source}
word_set.discard(source)
while wavefront:
next_front = set()
for u in wavefront:
for v in self.adj_list(u, word_set):
next_front.add(v)
word_set.remove(v)
wavefront = next_front
yield wavefront
def ladderLength(self, beginWord: str, endWord: str, wordList: List[str]) -> int:
if endWord not in wordList:
# Even if endWord isn't in the wordList
# the back BFS will start with endWord
# and may falsely declare a path.
return 0
step = 1
front, back = {beginWord}, {endWord}
front_bfs, back_bfs = self.bfs(beginWord, wordList), self.bfs(endWord, wordList)
while front:
if len(front) > len(back):
front, back = back, front
front_bfs, back_bfs = back_bfs, front_bfs
front = next(front_bfs)
if front & back:
return step+1
step += 1
return 0
Leave a comment