Recursive
Each node has three coordinates: row, col, val. The problem is to sort the node-values by its coordinates: column id, row id and value.
We emit column values in sorted order: start with lowest column id and go towards highest. Tracking column id is easy: if has
col, its left child has (col-1) and its right child has (col+1). Within a column, the values would be sorted by row id (or depth). However, if more than one values have same (row_id, column_id) we need to break the tie by value.
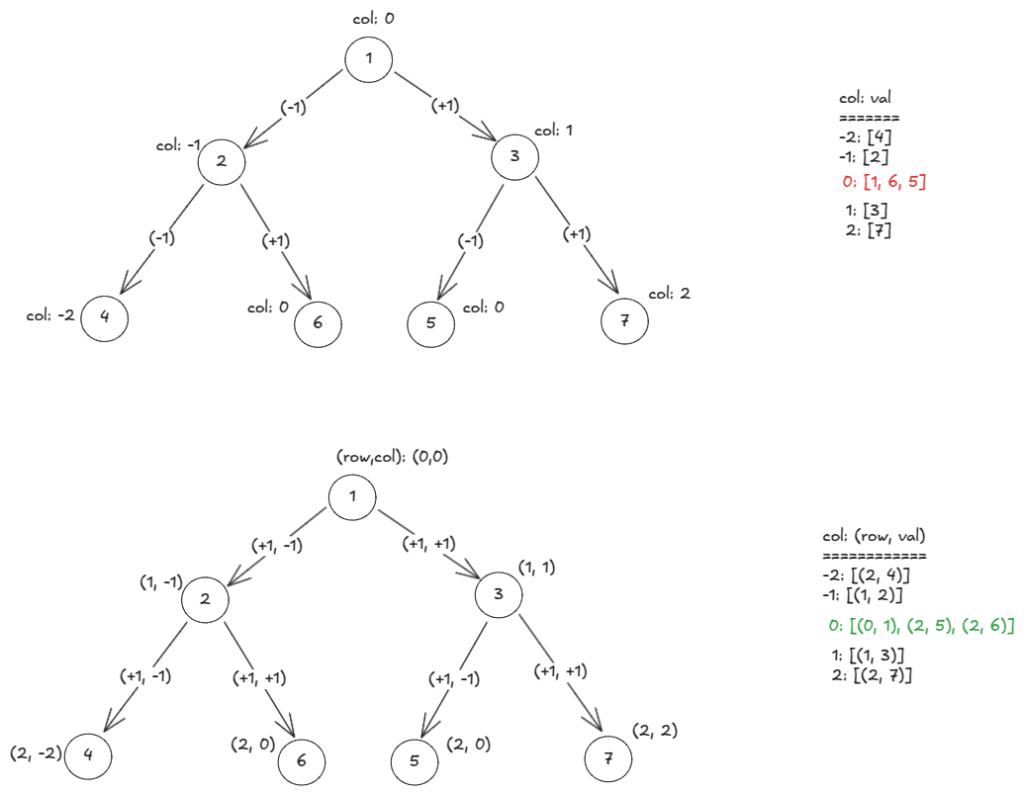
With a single DFS, we can collect the pairs (row_id, val) per column. We then emit columns in sorted order and within a column, we emit the pairs (just val) in sorted order. In that way, within a column, sorting’s primary key is row_id and secondary key is val.
Time: , space:
.
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def dfs(self, u, row, col, col_values) -> None:
if not u:
return
col_values[col] = col_values.get(col, []) + [(row, u.val)]
self.dfs(u.left, row+1, col-1, col_values)
self.dfs(u.right, row+1, col+1, col_values)
def verticalTraversal(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[List[int]]:
col_values = {}
self.dfs(root, 0, 0, col_values)
vertical = []
for col in sorted(col_values):
vertical.append( [ val for row, val in sorted(col_values[col]) ] )
return vertical
Iterative
To collect column’s (row, val) pairs we could also use BFS.
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def verticalTraversal(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[List[int]]:
if not root:
return []
col_values = {}
row = 0
# [ (node, col) ]
q = deque([(root, 0)])
while q:
level_len = len(q)
for _ in range(level_len):
u, col = q.popleft()
col_values[col] = col_values.get(col, []) + [(row, u.val)]
if u.left:
q.append( (u.left, col-1) )
if u.right:
q.append( (u.right, col+1) )
row += 1
vertical = []
for col in sorted(col_values):
vertical.append( [ val for row, val in sorted(col_values[col]) ] )
return vertical
Leave a comment