Substrings
For each of the substrings, check if it is in the
word_set.
Say ,
, and the longest word has length
. Time:
, space:
.
class Solution:
def indexPairs(self, text: str, words: List[str]) -> List[List[int]]:
word_set = set(words)
text_words = []
for i in range(len(text)):
for j in range(i, len(text)):
if text[i:j+1] in word_set:
text_words.append([i, j])
return text_words
Trie
If a word is in the text, the word is a prefix of a suffix of the text. Since the text has only suffixes, from a trie of
words, we can efficiently find the prefixes of these suffixes.
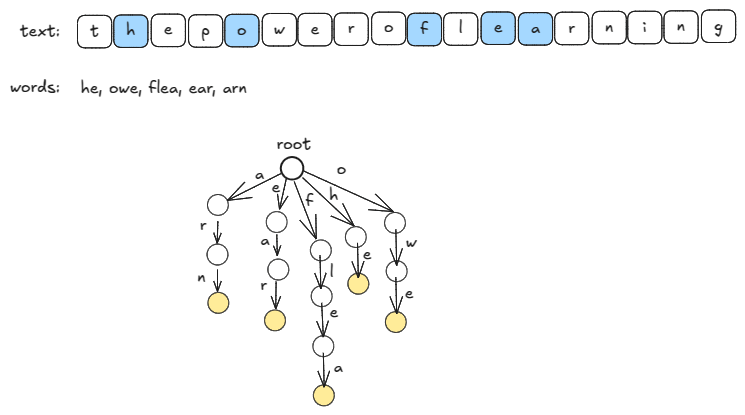
Building the trie takes time . Each
prefix_of() takes time .
Time: , space:
.
class TrieNode:
def __init__(self):
self.end_of_word = False
self.edges = {}
class Trie:
def __init__(self):
self.root = TrieNode()
def insert(self, word):
u = self.root
for char in word:
if char not in u.edges:
u.edges[char] = TrieNode()
u = u.edges[char]
u.end_of_word = True
def prefix_of(self, word, begin_index):
prefix_ends = []
u = self.root
for i in range(begin_index, len(word)):
char = word[i]
if char not in u.edges:
break
u = u.edges[char]
if u.end_of_word:
prefix_ends.append([begin_index, i])
return prefix_ends
class Solution:
def indexPairs(self, text: str, words: List[str]) -> List[List[int]]:
trie = Trie()
for w in words:
trie.insert(w)
text_words = []
for suffix_begin in range(len(text)):
prefixes = trie.prefix_of(text, suffix_begin)
if not prefixes:
continue
text_words.extend(prefixes)
return text_words
Leave a comment