Since a tie for the maximum frequency must be broken in favor of recent-most value, we should maintain LIFO order per frequency.
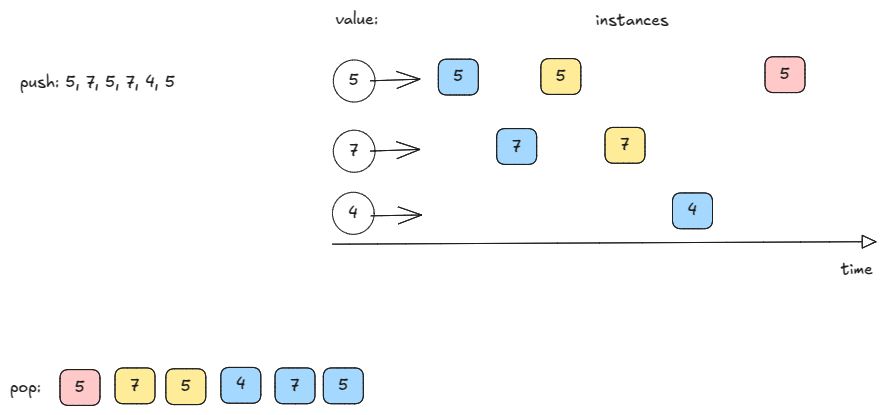
So, we need to maintain a stack per color. We shall use the below three pieces of information:
- A map from frequency to stack of values
- This lets us pop the recent-most value for a given frequency
- A map from value to its frequency
- This lets us push the value to the correct stack from (1)
- A variable
max_frequency- Since the maximum frequency does not jump, it grows like 1, 2, 3, … or decays like 3, 2, 1, we can easily track the current maximum frequency — saving us from searching for the max in the
dictfrom (1).
- Since the maximum frequency does not jump, it grows like 1, 2, 3, … or decays like 3, 2, 1, we can easily track the current maximum frequency — saving us from searching for the max in the
Say there are numbers in the
FreqStack having distinct values. So,
.
| Operation | Time | Space |
__init__ | ||
push | ||
pop |
class FreqStack:
def __init__(self):
self.freq_stack = {}
self.count = {}
self.max_freq = -1
def push(self, val: int) -> None:
self.count[val] = self.count.get(val, 0) + 1
f = self.count[val]
if f not in self.freq_stack:
self.freq_stack[f] = []
self.freq_stack[f].append(val)
self.max_freq = max(self.max_freq, f)
def pop(self) -> int:
v = self.freq_stack[self.max_freq].pop()
if not self.freq_stack[self.max_freq]:
self.max_freq -= 1
self.count[v] -= 1
return v
# Your FreqStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = FreqStack()
# obj.push(val)
# param_2 = obj.pop()
We can also implement FreqStack as a stack of stacks. We push a value onto a frequency-appropriate stack or we push a stack onto the stack of stacks. Similarly, we pop value from the top stack or if top stack is empty we pop it from the stack of stacks.
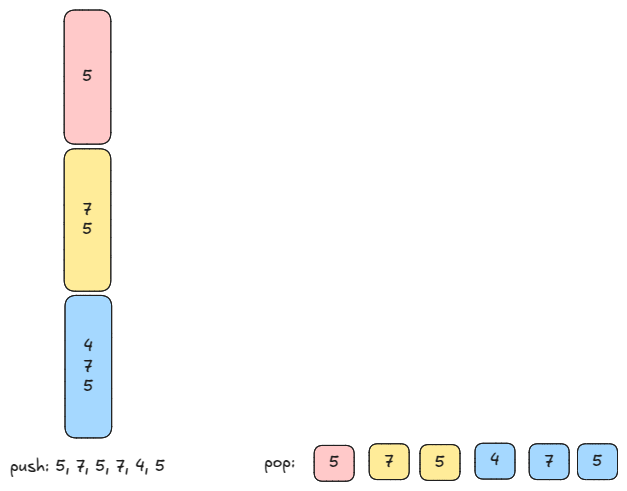
class FreqStack:
def __init__(self):
self.stacks = []
self.count = {}
def push(self, val: int) -> None:
self.count[val] = self.count.get(val, 0) + 1
f = self.count[val]
if f > len(self.stacks):
self.stacks.append([])
self.stacks[f-1].append(val)
def pop(self) -> int:
v = self.stacks[-1].pop()
if not self.stacks[-1]:
self.stacks.pop()
self.count[v] -= 1
return v
# Your FreqStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = FreqStack()
# obj.push(val)
# param_2 = obj.pop()
Leave a comment