We keep the below three pieces of information:
snapshot_id: Initialized with -1. On each snap, increases by 1.diff: A dict: {index -> value}. Captures changes since the lastsnap().snapshots: A dict: {snapshot_id -> diff}. If diff is empty, against the new snapshot_id, we save a reference to the previous snapshot’s diff. Otherwise, a copy of the diff is saved.
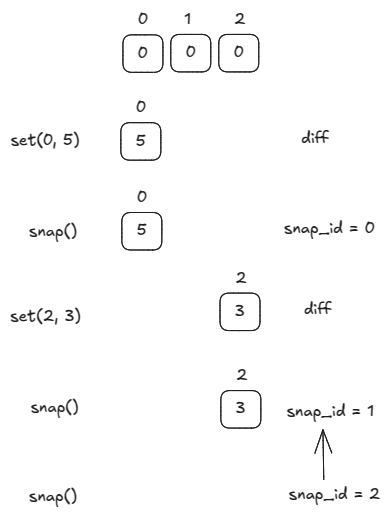
On get(), we may need to search through earlier snapshots to get the value at an index that has not changed for a while.
Say
snap‘s have been called.
| Operation | Time | Space |
__init__ | ||
set | ||
snap | ||
get |
class SnapshotArray:
def __init__(self, length: int):
self.snapshot_id = -1
self.diff = {}
self.snapshots = {}
def set(self, index: int, val: int) -> None:
self.diff[index] = val
def snap(self) -> int:
self.snapshot_id += 1
if self.diff:
self.snapshots[self.snapshot_id] = dict(self.diff)
self.diff = {}
else:
self.snapshots[self.snapshot_id] = (
self.snapshots[self.snapshot_id - 1] if self.snapshot_id > 0 else None
)
return self.snapshot_id
def get(self, index: int, snap_id: int) -> int:
while snap_id >= 0:
if not self.snapshots[snap_id]:
return 0
if index in self.snapshots[snap_id]:
return self.snapshots[snap_id][index]
snap_id -= 1
return 0
# Your SnapshotArray object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = SnapshotArray(length)
# obj.set(index,val)
# param_2 = obj.snap()
# param_3 = obj.get(index,snap_id)
Leave a comment