For skyline, building roofs are important.
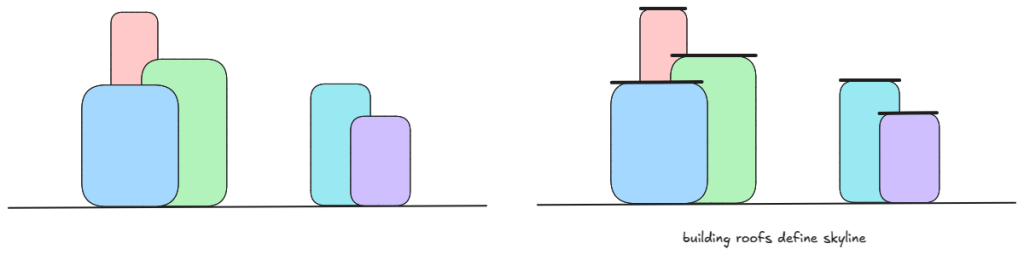
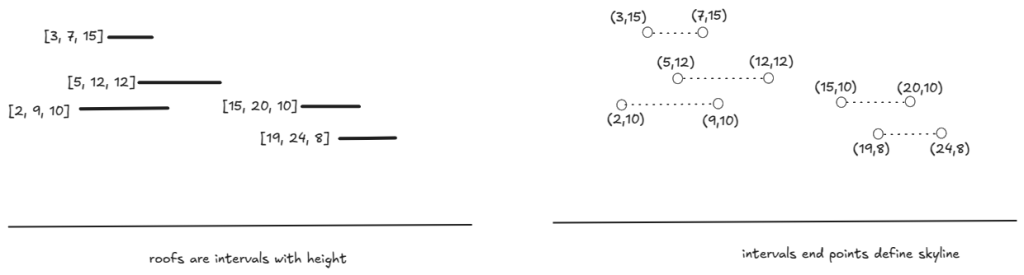
Roofs are intervals at some height.
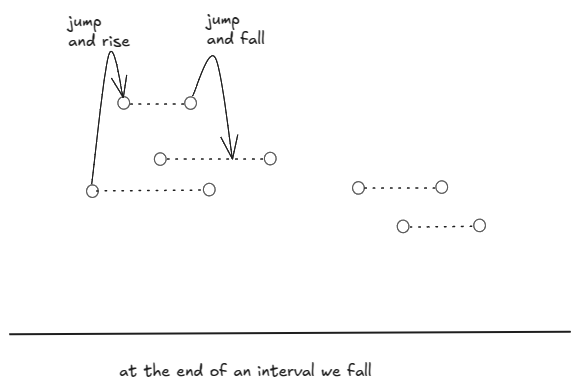
If we jump from the end of a roof, we fall to the next higher roof or we fall to the ground.
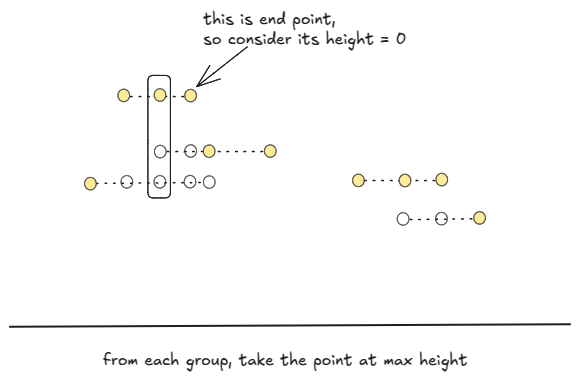
We can find the skyline points from the groups of heights at different locations — from each group, just take the point at the maximum height.
In the end, we can merge consecutive points at the same height.
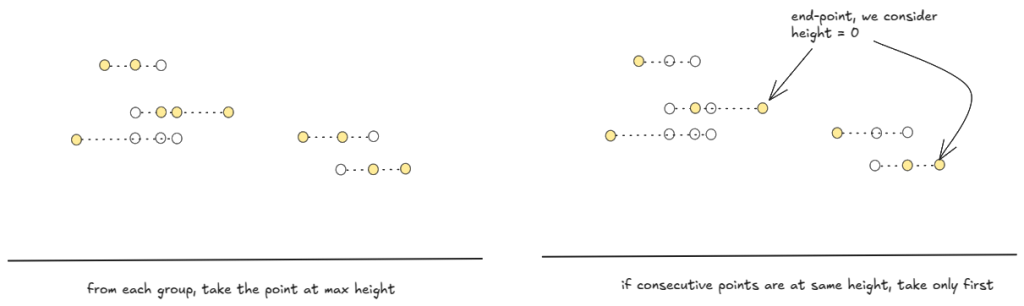
Linear scan and groups
For each building-endpoint, to find co-located heights, we do linear scan.
If there are buildings, time:
, space:
.
class Solution:
def get_colocated_heights(self, loc, buildings):
heights = set()
for a, b, h in buildings:
if loc < a or loc > b:
continue
heights.add( 0 if loc == b else h )
return heights
def getSkyline(self, buildings: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
colocated_heights = {}
for a, b, h in buildings:
if a not in colocated_heights:
colocated_heights[a] = set()
colocated_heights[a].add( h )
colocated_heights[a].update( self.get_colocated_heights(a, buildings) )
if b not in colocated_heights:
colocated_heights[b] = set()
colocated_heights[b].add( 0 )
colocated_heights[b].update( self.get_colocated_heights(b, buildings) )
skyline = []
for loc in sorted(colocated_heights):
h = max( colocated_heights[loc] )
if skyline and skyline[-1][1] == h:
continue
skyline.append([loc, h])
return skyline
Linear scan and group max
For a location, we only need the maximum height.
Time: , space:
.
class Solution:
def get_max_height_at(self, loc, buildings):
max_height = 0
for a, b, h in buildings:
if loc < a or loc > b:
continue
max_height = max(max_height, 0 if loc == b else h)
return max_height
def getSkyline(self, buildings: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
max_height_at = {}
for a, b, h in buildings:
max_height_at[a] = self.get_max_height_at(a, buildings)
max_height_at[b] = self.get_max_height_at(b, buildings)
skyline = []
for loc in sorted(max_height_at):
h = max_height_at[loc]
if skyline and skyline[-1][1] == h:
continue
skyline.append([loc, h])
return skyline
List of all possible points
If we have a list of points [0, max(roof-ends)], for a roof [a, b, h] we can update the heights of all b-a+1 points in that list.
Say max(roof-ends) = and max(roof-width) =
.
Time: , space:
.
class Solution:
def getSkyline(self, buildings: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
right_most_loc = max( end for _, end, _ in buildings )
max_height_at = [float("-inf") for _ in range(right_most_loc+1)]
for a, b, h in buildings:
for loc in range(a, b):
max_height_at[loc] = max( max_height_at[loc], h )
max_height_at[b] = max( max_height_at[b], 0 )
skyline = []
for loc, h in enumerate(max_height_at):
if h == float("-inf"):
continue
if skyline and skyline[-1][1] == h:
continue
skyline.append([loc, h])
return skyline
Linear scan through roof end-points
We only need to update the roof endpoint locations. So, for a roof [left, right], instead of updating all points, we can update only existent roof endpoints in [left, right].
Time: , space:
.
class Solution:
def getSkyline(self, buildings: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
max_height_at = {}
for left, right, h in buildings:
if left not in max_height_at:
max_height_at[left] = h
else:
max_height_at[left] = max( max_height_at[left], h )
if right not in max_height_at:
max_height_at[right] = 0
for left, right, h in buildings:
for loc in max_height_at:
if loc < left or loc >= right:
continue
max_height_at[loc] = max( max_height_at[loc], h )
skyline = []
for loc in sorted(max_height_at):
h = max_height_at[loc]
if skyline and skyline[-1][1] == h:
continue
skyline.append( [loc, h] )
return skyline
Binary search in roof-endpoints
Instead of linear scan, we could binary-search the roof end points.
Time: , space:
.
class Solution:
def find_location(self, x, locations):
lo, hi = 0, len(locations)-1
while lo <= hi:
mid = (lo + hi) // 2
if x == locations[mid]:
return mid
if locations[mid] < x:
lo = mid+1
else:
hi = mid-1
return -1
def getSkyline(self, buildings: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
max_height_at = {}
for left, right, h in buildings:
if left not in max_height_at:
max_height_at[left] = h
else:
max_height_at[left] = max( max_height_at[left], h )
if right not in max_height_at:
max_height_at[right] = 0
locations = sorted(x for x in max_height_at)
for left, right, h in buildings:
left_pos = self.find_location(left, locations)
right_pos = self.find_location(right, locations)
for i in range(left_pos, right_pos):
loc = locations[i]
max_height_at[loc] = max( max_height_at[loc], h )
skyline = []
for loc in locations:
h = max_height_at[loc]
if skyline and skyline[-1][1] == h:
continue
skyline.append( [loc, h] )
return skyline
Leave a comment