Stack of (num, curr_max)
We can keep current max with the element.
Say len(stack) = .
| Operation | Time | Space |
__init__ | ||
push | ||
pop | ||
top | ||
peekMax | ||
popMax |
class MaxStack:
def __init__(self):
self.stack = []
def push(self, x: int) -> None:
if not self.stack:
self.stack.append( [x, x] )
return
_, top_max = self.stack[-1]
curr_max = max(top_max, x)
self.stack.append( [x, curr_max] )
def pop(self) -> int:
x, _ = self.stack.pop()
return x
def top(self) -> int:
x, _ = self.stack[-1]
return x
def peekMax(self) -> int:
_, top_max = self.stack[-1]
return top_max
def popMax(self) -> int:
_, curr_max = self.stack[-1]
peeks = []
while self.stack and self.stack[-1][0] != self.stack[-1][1]:
peeks.append( self.stack[-1][0] )
self.stack.pop()
self.stack.pop()
while peeks:
self.push(peeks.pop())
return curr_max
# Your MaxStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = MaxStack()
# obj.push(x)
# param_2 = obj.pop()
# param_3 = obj.top()
# param_4 = obj.peekMax()
# param_5 = obj.popMax()
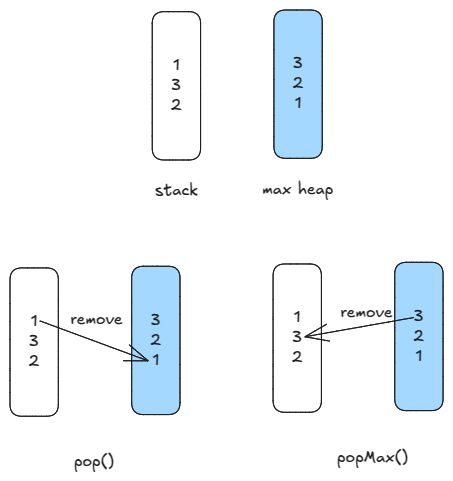
Above, in the worst-case, popMax() needs to sift through the entire stack. To make finding max faster, we can use max heap.
LinkedList and Max-Heap
We keep two stacks: one for values and one for maxes. For maxes, we use a max heap with the value as the primary key and an increasing id as the secondary key.
On popMax(), we need to remove the latest max from the value stack as well. The latest max may appear in the middle of the value stack and deleting it creates a hole. So, we use a LinkedList as the value stack. Similarly, when we pop(), we need to remove the top from the max heap. Since, max-heap does not support efficient delete, we just mark the item as deleted. When we do peekMax() or popMax() again, we get rid of the tops which are marked as deleted.
| Operation | Time | Space |
__init__ | ||
push | ||
pop | ||
top | ||
peekMax | ||
popMax |
popMax or peekMax has amortized time . Say we made
pushes. Now, we did
pops. We do a
popMax. It can trigger pops from the max heap which has total cost
, so per push the cost is amortized to
.
from heapq import heappush as push, heappop as pop
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.prev, self.next = None, None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head, self.tail = None, None
def append(self, node):
if not self.tail:
self.tail = node
self.head = node
return
self.tail.next = node
node.prev = self.tail
self.tail = self.tail.next
def top(self):
return self.tail
def pop(self):
node = self.tail
if not self.tail.prev:
self.tail = None
self.head = None
return node
self.tail = self.tail.prev
self.tail.next = None
return node
def remove(self, node):
prev_node, next_node = node.prev, node.next
if not prev_node:
# node is head
self.head = self.head.next
if self.head:
self.head.prev = None
else:
self.tail = None
node.prev, node.next = None, None
return
if not next_node:
# node is tail
self.tail = self.tail.prev
self.tail.next = None
node.prev, node.next = None, None
return
prev_node.next = next_node
next_node.prev = prev_node
node.prev, node.next = None, None
class MaxStack:
def __init__(self):
self.deleted_nodes = set()
self.id = -1
self.stack = LinkedList()
self.maxq = []
def push(self, x: int) -> None:
self.id += 1
node = ListNode(x)
self.stack.append(node)
push( self.maxq, (-x, -self.id, node) )
def pop(self) -> int:
node = self.stack.pop()
self.deleted_nodes.add(node)
return node.val
def top(self) -> int:
top_node = self.stack.top()
return top_node.val
def __remove_stale_nodes(self):
while self.maxq:
*_, node = self.maxq[0]
if node not in self.deleted_nodes:
break
pop(self.maxq)
self.deleted_nodes.remove(node)
def peekMax(self) -> int:
self.__remove_stale_nodes()
neg_x, *_ = self.maxq[0]
return -neg_x
def popMax(self) -> int:
self.__remove_stale_nodes()
neg_x, _, node = pop(self.maxq)
self.stack.remove(node)
return -neg_x
# Your MaxStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = MaxStack()
# obj.push(x)
# param_2 = obj.pop()
# param_3 = obj.top()
# param_4 = obj.peekMax()
# param_5 = obj.popMax()
LinkedList and Updatable Max-Heap
Above, if we do not call popMax for a while, the heap operations can get slow.
If our max heap supported updating key in time, instead of marking it deleted, we could update the key to
and then do a pop from the max heap. This ensures, instead of amortized, every popMax has time
.
Leave a comment