Since we have parent pointer, we can find the path from p -> root and q -> root and then traverse the two paths in sync to find the LCA.
Time: , space:
.
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.parent = None
"""
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, p: 'Node', q: 'Node') -> 'Node':
p_path = []
curr = p
while curr:
p_path.append(curr)
curr = curr.parent
q_path = []
curr = q
while curr:
q_path.append(curr)
curr = curr.parent
short_path, long_path = (p_path, q_path) if len(p_path) <= len(q_path) else (q_path, p_path)
i, j = 0, len(long_path)-len(short_path)
while short_path[i] != long_path[j]:
i += 1
j += 1
return short_path[i]
We do not need to precompute the paths. Say p and q are traversing towards the root. Below, by the time p reaches root, q is just nodes behind. So, if we can make
p take a detour of extra nodes, then
p and q will be synced and later they will meet at LCA.
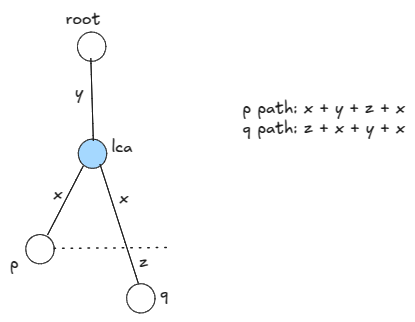
Time: , space:
.
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.parent = None
"""
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, p: 'Node', q: 'Node') -> 'Node':
a, b = p, q
while a != b:
a = a.parent or q
b = b.parent or p
return a
Leave a comment