Two pass
From the length of the list we find how many -groups need to be reversed and we reverse each
-group in sequence. While reversing a
-group, we have two types of operations:
- Within-group: All nodes within the group need to be reversed.
- Across-group: The connection from previous group to current group and the connection from the current group to next group need fixing.
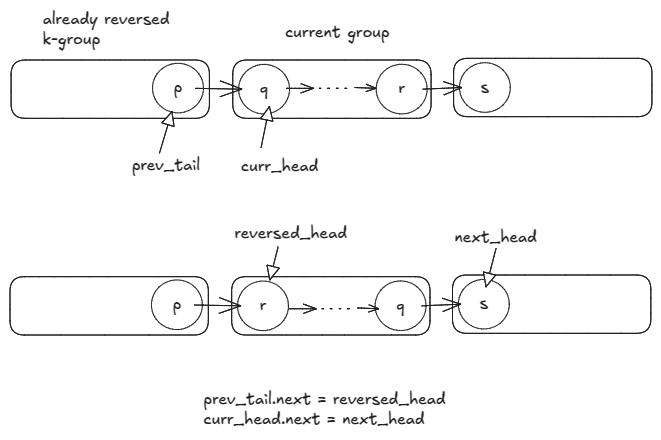
Time: , space:
.
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverse(self, head, k):
prev, curr = None, head
while k > 0:
next = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = next
k -= 1
return prev, curr
def reverseKGroup(self, head: Optional[ListNode], k: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
list_len = 0
t = head
while t:
list_len += 1
t = t.next
group_count = list_len // k
list_head = None
prev_tail = None
curr_head = head
while group_count > 0:
reversed_head, next_head = self.reverse(curr_head, k)
if prev_tail:
prev_tail.next = reversed_head
curr_head.next = next_head
prev_tail = curr_head
curr_head = next_head
list_head = list_head or reversed_head
group_count -= 1
return list_head
One pass
While reversing a -group, if
nodes got reversed where
, we know we have a tail group which we can restore back by one more
-reverse. In that way, we can get rid of the initial pass to find
group_count.
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverse(self, head, k):
m = 0
prev, curr = None, head
while k > 0 and curr:
next = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = next
k -= 1
m += 1
return prev, curr, m
def reverseKGroup(self, head: Optional[ListNode], k: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
prev_tail = None
list_head = None
curr_head = head
while True:
reversed_head, next_head, reverse_count = self.reverse(curr_head, k)
if reverse_count < k:
self.reverse(reversed_head, reverse_count)
break
if prev_tail:
prev_tail.next = reversed_head
prev_tail = curr_head
curr_head.next = next_head
curr_head = next_head
list_head = list_head or reversed_head
return list_head
Leave a comment